Recientemente, los precios del carbonato de litio se han disparado, y las empresas de almacenamiento de energía están nuevamente ocupadas calculando la rentabilidad de sus inversiones. Esta volatilidad anormal de precios finalmente ha impactado el segmento de aplicaciones del mercado de almacenamiento de energía.
Vale la pena señalar que muchas empresas de almacenamiento de energía ya no aceptan pasivamente estas fluctuaciones de los precios de las materias primas; en cambio, están optando por participar activamente en el comercio de futuros de carbonato de litio, y algunas empresas incluso han obtenido ganancias adicionales como resultado.
¿Fluctuaciones irracionales en los futuros del carbonato de litio?
Desde junio de 2025, el precio del carbonato de litio ha experimentado un aumento cada vez mayor, y en 2026 ha aumentado día a día. El 5 de enero, alcanzó los 133.000 yuanes/tonelada; el 6 de enero, los 141.300 yuanes/tonelada; el 7 de enero, superó los 150.000 yuanes/tonelada; y el 12 de enero, los 156.000 yuanes/tonelada. Según las últimas noticias del 13 de enero, el principal contrato de futuros de carbonato de litio alcanzó su límite superior, con un aumento diario del 12%, cerrando en 179.000 yuanes/tonelada.
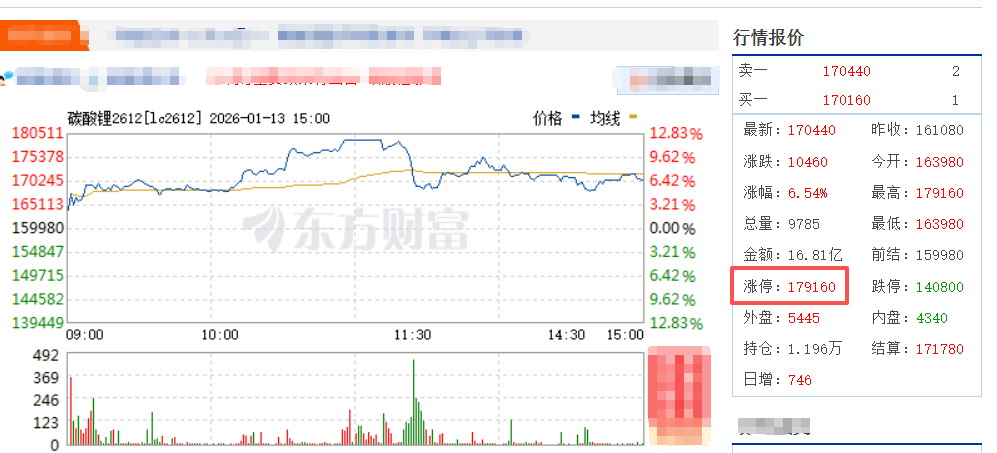
Como materia prima fundamental para el almacenamiento de energía en baterías, los futuros de carbonato de litio impactarán la producción y operación de la industria del almacenamiento de energía, los modelos de precios, el panorama competitivo y la sinergia de la cadena de suministro a través de la orientación de precios, la gestión de riesgos y la asignación de recursos. En primer lugar, determinarán las expectativas de precios a largo plazo, guiando el ritmo de expansión de las empresas mineras de litio upstream y ajustando los niveles de inventario de las empresas midstream y downstream, lo que afectará los cálculos de viabilidad económica de los proyectos de almacenamiento de energía. En segundo lugar, algunas empresas relacionadas con baterías de litio utilizarán futuros de carbonato de litio como cobertura, fijando los precios de compra de la materia prima y asegurando la rentabilidad bruta. En tercer lugar, forzarán la salida de capacidad de producción ineficiente en la industria del almacenamiento de energía.
Por el contrario, si los precios de los futuros de carbonato de litio se ven impulsados al alza por compras y ventas especulativas a corto plazo, las señales erróneas pueden provocar una expansión desordenada de la capacidad, altos costos de negociación y la supresión de la demanda aguas abajo. Para la industria del almacenamiento de energía, esto podría provocar un colapso de precios a corto plazo y afectar la capacidad instalada a largo plazo.
Desde la perspectiva de la oferta y la demanda, sumado a múltiples factores como las políticas del mercado de almacenamiento de energía, el crecimiento explosivo de la demanda de almacenamiento de energía y las brechas de suministro a corto plazo, es probable que la oferta de carbonato de litio siga mostrando una tendencia de "equilibrio ajustado". Sin embargo, según datos de la Bolsa de Futuros de Guangzhou y plataformas públicas, desde noviembre de 2025, los futuros de carbonato de litio han sido consistentemente superiores al precio spot más alto, y sus movimientos de precios se han mantenido "coordinados". En general, es normal que los precios de los futuros sean ligeramente superiores a los precios spot debido a factores como los costos de mantenimiento, pero la creciente brecha de precios debería alertar a la industria del almacenamiento de energía ante una "falsa prosperidad" causada por señales de precios que podrían desviarse de los fundamentos.
Para hacer frente de manera eficaz a la amenaza del continuo aumento de los precios del carbonato de litio, las empresas de la cadena industrial de almacenamiento de energía se han unido recientemente a las filas de los comerciantes de "futuros de carbonato de litio".
Según estadísticas incompletas de Polaris Energy Storage Network, desde noviembre de 2025, 16 empresas que cotizan en bolsa han declarado participar en operaciones de cobertura de futuros de carbonato de litio, con un valor de contrato superior a 100 000 millones de yuanes. El ámbito de negocio de estas empresas abarca materiales upstream, baterías midstream e integradores de almacenamiento de energía downstream, entre ellos Trina Solar, TBEA, Canadian Solar, Penghui Energy, Farasis Energy, Tianli Lithium Energy, Rongjie Energy, Do-Fluoride Chemicals, Mengguli, Hainan Mining, Jiangte Motor, Nanhua Bioengineering, Tinci Materials, Tianji Energy, Wanrun New Energy y Xinzhoubang. (Ordenados por tipo de negocio, sin orden específico).
Entre ellos, Trina Solar, TBEA y Canadian Solar, tres integradores de almacenamiento de energía, afirmaron que el propósito de realizar negocios de cobertura de futuros es reducir las muchas incertidumbres y riesgos generados por la fluctuación de los precios de las materias primas para la producción y operación de la empresa, evitar riesgos de precios, garantizar la entrega oportuna de los productos, controlar los costos de los productos y asegurar las ganancias de las ventas de los proyectos.
Vale la pena mencionar que Canadian Solar afirmó que el plazo desde la firma hasta la entrega de los contratos comerciales de almacenamiento de energía varía de 6 a 15 meses, y los precios de todos los contratos se determinan al comienzo del período, lo que puede fijar costos o ganancias por adelantado.
Los precios de futuros del carbonato de litio han aumentado más del 166,6% en los últimos seis meses.
Si el precio de futuros supera el precio al contado por un margen significativo, más allá del rango normal de costos de mantenimiento, esto podría indicar fluctuaciones irracionales de precios, a menudo impulsadas por capital especulativo. Según informes públicos, para finales de 2025, el capital especulativo representaba hasta el 52 % del mercado de futuros de carbonato de litio, superando al capital industrial.
La participación del capital industrial en la cobertura puede ayudar a orientar los precios de futuros hacia los fundamentos del mercado spot, frenando las fluctuaciones irracionales de precios que se desvían de la oferta y la demanda, y devolviendo los precios a los fundamentos. La lógica fundamental es que las minas de litio y los proveedores de materiales upstream, los fabricantes de baterías midstream y las empresas de almacenamiento de energía downstream de la cadena de la industria del carbonato de litio participan en futuros no para "apostar a las fluctuaciones de precios", sino para asegurar los costos o beneficios de producción y operación, mitigar los riesgos de volatilidad de precios, y su comportamiento comercial está totalmente anclado a la oferta y la demanda spot.
Para la industria, la participación del capital industrial en la cobertura puede frenar las fluctuaciones irracionales de precios; a las empresas, les permite asegurar con antelación los costos de adquisición de materias primas, mitigar el riesgo de aumento de los precios spot y compensar dicho aumento con las ganancias de la negociación de futuros, logrando así rentabilidad. Penghui Energy reveló que, del 16 de mayo de 2025 al 31 de diciembre de 2025, el importe acumulado de ingresos reconocidos por la cobertura de futuros de materias primas fue de aproximadamente 14,2337 millones de RMB.
Las persistentes fluctuaciones irracionales en los precios del carbonato de litio han afectado gravemente el desarrollo sostenible de la cadena industrial, lo que ha impulsado a la Bolsa de Futuros de Guangzhou (GFE) a intensificar sus esfuerzos regulatorios. El 12 de enero, la GFE emitió un aviso de autorregulación que impuso una restricción de tres meses a seis clientes sospechosos de no declarar sus relaciones de control reales según lo requerido y de exceder los límites de negociación en contratos de futuros de carbonato de litio. Con las medidas de autorregulación adoptadas el 26 de diciembre de 2025 y el 8 de enero de 2026, el número total de casos investigados asciende a tres en menos de un mes.
El 7 de enero, el Ministerio de Industria y Tecnología de la Información, la Comisión Nacional de Desarrollo y Reforma, la Administración Estatal de Regulación del Mercado y la Administración Nacional de Energía celebraron conjuntamente un simposio sobre la industria de baterías de almacenamiento de energía y potencia, mencionando orientar a las empresas para asignar científicamente la capacidad de producción y promover la construcción de un orden de mercado basado en alta calidad y competencia leal.
La tendencia del precio del carbonato de litio debe basarse en la relación real entre la oferta y la demanda, y la prosperidad de la industria de almacenamiento de energía debe basarse en la racionalidad para garantizar el desarrollo constante y a largo plazo de la industria.